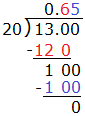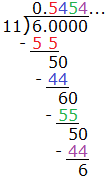Real Numbers
8th Grade
|
|
|
Alabama Course of Study Standards:
1
|
Define the real number system as composed of rational and irrational numbers.- Explain that every number has a decimal expansion; for rational numbers, the decimal expansion repeats or terminates.
- Convert a decimal expansion that repeats into a rational number.
|
Arizona Academic Standards:
8.NS.A.1
|
Know that numbers that are not rational are called irrational. Understand informally that every number has a decimal expansion. Know that numbers whose decimal expansions do not terminate in zeros or in a repeating sequence of fixed digits are called irrational. |
Common Core State Standards:
Math.8.NS.1 or 8.NS.A.1
|
Know that numbers that are not rational are called irrational. Understand informally that every number has a decimal expansion; for rational numbers show that the decimal expansion repeats eventually, and convert a decimal expansion which repeats eventually into a rational number. |
Georgia Math and ELA Standards:
8.NR.1.1
|
Distinguish between rational and irrational numbers using decimal expansion. Convert a decimal expansion which repeats eventually into a rational number. |
North Carolina - Standard Course of Study:
8.NS.1
|
Understand that every number has a decimal expansion. Building upon the definition of a rational number, know that an irrational number is defined as a non-repeating, non-terminating decimal. |
New York State Next Generation Learning Standards:
8.NS.1
|
Understand informally that every number has a decimal expansion; for rational numbers show that the decimal expansion eventually repeats. Know that other numbers that are not rational are called irrational. |
Alabama Course of Study Standards:
2
|
Locate rational approximations of irrational numbers on a number line, compare their sizes, and estimate the values
of the irrational numbers. |
Arizona Academic Standards:
8.NS.A.2
|
Use rational approximations of irrational numbers to compare the size of irrational numbers. Locate them approximately on a number line diagram, and estimate their values. |
Common Core State Standards:
Math.8.NS.2 or 8.NS.A.2
|
Use rational approximations of irrational numbers to compare the size of irrational numbers, locate them approximately on a number line diagram, and estimate the value of expressions (e.g., 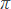 2). For example, by truncating the decimal expansion of √2, show that √2 is between 1 and 2, then between 1.4 and 1.5, and explain how to continue on to get better approximations. 2). For example, by truncating the decimal expansion of √2, show that √2 is between 1 and 2, then between 1.4 and 1.5, and explain how to continue on to get better approximations.
|
Georgia Math and ELA Standards:
8.NR.1.2
|
Approximate irrational numbers to compare the size of irrational numbers, locate them approximately on a number line, and estimate the value of expressions. |
North Carolina - Standard Course of Study:
8.NS.2
|
Use rational approximations of irrational numbers to compare the size of irrational numbers and locate them approximately on a number line. Estimate the value of expressions involving:- Square roots and cube roots to the tenths.
 to the hundredths. to the hundredths.
|
New York State Next Generation Learning Standards:
8.NS.2
|
Use rational approximations of irrational numbers to compare the size of irrational numbers, locate them approximately on a number line, and estimate the value of expressions. |
Wisconsin Academic Standards:
8.NS.A.2
|
Use rational approximations of irrational numbers to compare the size of irrational numbers, locate them approximately on a number line, and estimate the value of expressions (e.g., 2).
For example, by truncating the decimal expansion of √2, show that √2 is between 1 and 2, then between 1.4 and 1.5, and explain how to continue on to get better approximations. |
Pennsylvania Core Standards:
CC.2.1.8.E.1
|
Distinguish between rational and irrational numbers using their properties. |
Pennsylvania Core Standards:
M08.A-N.1.1.1
|
Determine whether a number is rational or irrational. For rational numbers, show that the decimal expansion terminates or repeats (limit repeating decimals to thousandths). |
Pennsylvania Core Standards:
M08.A-N.1.1.2
|
Convert a terminating or repeating decimal to a rational number (limit repeating decimals to thousandths). |
Pennsylvania Core Standards:
CC.2.1.8.E.4
|
Estimate irrational numbers by comparing them to rational numbers. |
Pennsylvania Core Standards:
M08.A-N.1.1.3
|
Estimate the value of irrational numbers without a calculator (limit whole number radicand to less than 144). |
Pennsylvania Core Standards:
M08.A-N.1.1.4
|
Use rational approximations of irrational numbers to compare and order irrational numbers. |
Pennsylvania Core Standards:
M08.A-N.1.1.5
|
Locate/identify rational and irrational numbers at their approximate locations on a number line |
Florida - Benchmarks for Excellent Student Thinking:
MA.8.NSO.1.1
|
Extend previous understanding of rational numbers to define irrational numbers within the real number system. Locate an approximate value of a numerical expression involving irrational numbers on a number line. |
Florida - Benchmarks for Excellent Student Thinking:
MA.8.NSO.1.2
|
Plot, order and compare rational and irrational numbers, represented in various forms |
Georgia Math and ELA Standards:
8.NR.1.1
|
Distinguish between rational and
irrational numbers using decimal
expansion. Convert a decimal
expansion which repeats eventually
into a rational number. |
Georgia Math and ELA Standards:
8.NR.1.2
|
Approximate irrational numbers to
compare the size of irrational
numbers, locate them approximately
on a number line, and estimate the
value of expressions. |
Arkansas Academic Standards:
8.NCC.1
|
Describe relationships in the real number system (rational and irrational).- Numbers relationships to include: decimal expansion for rational and irrational numbers, square roots of nonperfect squares, and cube roots of nonperfect cubes
|
Arkansas Academic Standards:
8.NCC.2
|
Compare the size of irrational numbers and locate them on a number line by finding the rational approximations. |
|
|


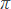 to the hundredths.
to the hundredths. 8th Grade Math - Real Numbers Lesson
8th Grade Math - Real Numbers Lesson